Explore the comprehensive guide on Fluconazole – an antifungal medication used to treat various fungal infections. Learn about its uses, mechanism of action, dosage, side effects, contraindications, brand names, and price.
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of Action
3. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
4. Indications
5. Drug of Choice
6. Contraindications
7. Side Effects
8. Drug Interactions
9. Dosage
10. Brand Names and Price
11. Conclusion
1. Introduction:
Fluconazole is a widely used *triazole antifungal agent* effective against various fungal infections. It is particularly used in treating *candidiasis*, *cryptococcal meningitis*, and as prophylaxis in immunocompromised individuals, such as those with HIV/AIDS or cancer.
2. Mechanism of Action:
Fluconazole inhibits the fungal cytochrome P450 enzyme *14α-demethylase*, which is necessary for converting lanosterol to ergosterol — a critical component of the fungal cell membrane. The disruption of this process leads to increased cell permeability and ultimately cell death.
3. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics:
- *Absorption:* Excellent oral bioavailability (~90%)
- *Peak plasma time:* 1–2 hours
- *Half-life:* 30–36 hours
- *Distribution:* Widely distributed in body fluids, including CSF
- *Metabolism:* Minimal hepatic metabolism
- *Excretion:* Mainly renal
4. Indications:
- *Oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis*
- *Cryptococcal meningitis*
- *Dermatophytosis and tinea infections*
- *Fungal prophylaxis* in transplant or cancer patients
5. Drug of Choice:
- Vaginal candidiasis (single dose therapy)
- Cryptococcal meningitis (especially in HIV patients, in combination therapy)
- Oral and esophageal candidiasis
- Prophylaxis in neutropenic and HIV/AIDS patients
6. Contraindications:
- Known hypersensitivity to fluconazole or other azoles
- Caution in patients with *hepatic dysfunction*
- Avoid in patients on medications like *terfenadine* or *cisapride* (QT prolongation risk)
7. Side Effects:
- Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
- Headache
- Skin rashes
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Rare: hepatotoxicity, QT prolongation, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
8. Drug Interactions:
- *Warfarin:* Increased bleeding risk
- *Phenytoin, rifampin, cyclosporine:* Altered plasma levels
- *Oral hypoglycemics:* Risk of hypoglycemia
- *Theophylline:* Increased serum concentration
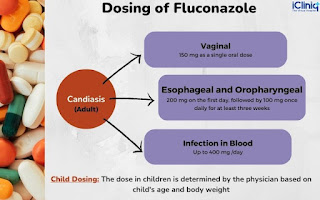
9. Dosage:
- *Vaginal candidiasis:* 150 mg single oral dose
- *Oropharyngeal candidiasis:* 100–200 mg once daily for 7–14 days
- *Cryptococcal meningitis:*
- Initial: 400 mg/day
- Maintenance: 200–400 mg/day for 8+ weeks
- *Prophylaxis:* 200–400 mg daily
- *Pediatric dose:* Based on weight and indication
10. Brand Names and Price:
Brand Names:
- Diflucan®️
- Fluzole®️
- Zocon®️
- Fungone®️
- Canazol®️
Price:
- 150 mg tablet: 1 to10 depending on brand and country
- Available in tablets, capsules, suspension, and IV form
11. Conclusion:
Fluconazole is a highly effective and versatile antifungal agent with a broad spectrum of activity and excellent safety profile when used appropriately. Its convenient oral and intravenous formulations make it suitable for both outpatient and inpatient settings. However, prolonged use requires liver monitoring and awareness of potential drug interactions







No comments:
Post a Comment
I will reply soon. Thanks for comment.